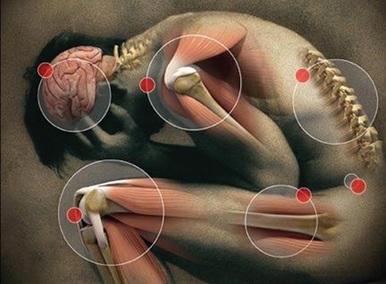
What is Chronic Pain?
|
This is a question asked often those who suffer pain, and sometimes not easy to answer. We know that pain is usually a body notice that something is wrong, but sometimes the system is broken and issues a warning signal that is unnecessary or disproportionate to the underlying disease. In fact, there is sometimes a warning sign of pain without really being a disease or injury.
Pain can be a friend or an enemy. The most common cause of pain is detected by the body of a tissue injury or the presence of a disease. The usual pain intensity responds more or less exactly to the severity of physical disorder. If the pain is relieved with simple analgesics, probably disappear in a few hours or days. If it is alarming to severe, should see a doctor as soon as possible. Some people have recurrent pain such as headaches or menstrual cramps, and know from experience that they will not have serious consequences, even annoying. When the alarm signal is strong pain, especially if the patient is unaware of its cause, the alarm system is serving its purpose and you have to take the warning seriously.
There is no particular time at which it can be stated that short-term pain has become chronic. Depends on the disease. In general terms, it is understood that there is chronic pain when it continues for more than six months and not relieved by medical or surgical treatments.
Chronic pain may also be due to active disease, as with back pain or leg (pain felt in the back or legs can be due to diseases of spine), complex regional pain syndrome (which usually occurs in the feet or hands after an injury such as a broken bone), pain following surgery (which caused nerve damage) or painful neuropathies (due to neurological injuries nerves that generate severe chronic pain)
Approximately 100 million Americans have reported that they suffer from severe chronic pain every year. Chronic pain is defined as pain which lasts from thirty days to six months at a time, and affects a person on a personal and professional level. Chronic pain can be caused by persistent back and neck pain, sciatica, fibrillation, and migraines. Other possible causes include pain related to cancer, depression, insomnia, arthritis, and pain after a surgical procedure. Currently, there are not many options available to help patients manage their pain levels short of drugs. Pills or Opioids and Injections are invasive to our body. Topical Pain Creams from a trusted Compound Pharmacy and and there are many non invasive pain treatments.
Pain can be a friend or an enemy. The most common cause of pain is detected by the body of a tissue injury or the presence of a disease. The usual pain intensity responds more or less exactly to the severity of physical disorder. If the pain is relieved with simple analgesics, probably disappear in a few hours or days. If it is alarming to severe, should see a doctor as soon as possible. Some people have recurrent pain such as headaches or menstrual cramps, and know from experience that they will not have serious consequences, even annoying. When the alarm signal is strong pain, especially if the patient is unaware of its cause, the alarm system is serving its purpose and you have to take the warning seriously.
There is no particular time at which it can be stated that short-term pain has become chronic. Depends on the disease. In general terms, it is understood that there is chronic pain when it continues for more than six months and not relieved by medical or surgical treatments.
Chronic pain may also be due to active disease, as with back pain or leg (pain felt in the back or legs can be due to diseases of spine), complex regional pain syndrome (which usually occurs in the feet or hands after an injury such as a broken bone), pain following surgery (which caused nerve damage) or painful neuropathies (due to neurological injuries nerves that generate severe chronic pain)
Approximately 100 million Americans have reported that they suffer from severe chronic pain every year. Chronic pain is defined as pain which lasts from thirty days to six months at a time, and affects a person on a personal and professional level. Chronic pain can be caused by persistent back and neck pain, sciatica, fibrillation, and migraines. Other possible causes include pain related to cancer, depression, insomnia, arthritis, and pain after a surgical procedure. Currently, there are not many options available to help patients manage their pain levels short of drugs. Pills or Opioids and Injections are invasive to our body. Topical Pain Creams from a trusted Compound Pharmacy and and there are many non invasive pain treatments.
Chronic Pain Does Not Discriminate
Anyone can suffer chronic pain. Usually presented as older adults or people with diseases such as diabetes, arthritis or back problems. Persistent pain is not a normal part of aging and treatment should be instituted. Chronic pain can not be prevented in all cases. However, early and aggressive treatment of sudden, severe pain can reduce the chances of chronic pain evolves. Certain conditions may increase the risk of chronic pain, such as amputation of a limb (phantom limb pain), arthritis or anxiety disorders. Lifestyle-unbalanced diets, smoking, alcohol or drugs, inactivity, also may predispose to chronic pain.
The intensity of pain that every person can suffer after apparently identical lesions is highly variable.There are people who have a lot, while others do not even need minor analgesics for pain relief. A particularly disturbing situation, but not uncommon, is the condition of a severe and persistent pain after a seemingly minor injury, like a paper cut. Do not know why this happens. Some people seem to have preset to pain, while others seem immune to it. These individual differences may respond in part to the education received or cultural traditions. However, there is increasing evidence that genes may also influence the response to pain. And of course, we can not control our genes.
"Pain is a major health problem in the United States. Although acute pain may reasonably be regarded as a symptom of a disease or injury, chronic and recurrent pain is a specific healthcare calamity, a disease in itself"
Anyone can suffer chronic pain. Usually presented as older adults or people with diseases such as diabetes, arthritis or back problems. Persistent pain is not a normal part of aging and treatment should be instituted. Chronic pain can not be prevented in all cases. However, early and aggressive treatment of sudden, severe pain can reduce the chances of chronic pain evolves. Certain conditions may increase the risk of chronic pain, such as amputation of a limb (phantom limb pain), arthritis or anxiety disorders. Lifestyle-unbalanced diets, smoking, alcohol or drugs, inactivity, also may predispose to chronic pain.
The intensity of pain that every person can suffer after apparently identical lesions is highly variable.There are people who have a lot, while others do not even need minor analgesics for pain relief. A particularly disturbing situation, but not uncommon, is the condition of a severe and persistent pain after a seemingly minor injury, like a paper cut. Do not know why this happens. Some people seem to have preset to pain, while others seem immune to it. These individual differences may respond in part to the education received or cultural traditions. However, there is increasing evidence that genes may also influence the response to pain. And of course, we can not control our genes.
"Pain is a major health problem in the United States. Although acute pain may reasonably be regarded as a symptom of a disease or injury, chronic and recurrent pain is a specific healthcare calamity, a disease in itself"
Chronic pain is often determined by the appearance of a complex set of physical and psycho social changes that are integral to the problem of chronic pain and greatly increase the burden of pain for the patient:
- immobility and, therefore, muscular dystrophies, joints, etc.
- depressed immune system and increased susceptibility to disease
- sleep disturbances
- lack of appetite and malnutrition
- dependence to medication
- reliance on family members and other caregivers
- excessive and inappropriate use of health care professionals systems
- poor performance at work or inability to work, disability
- isolation from society and family, introversion
- anxiety, fear
- anger, frustration, depression, suicide